astrojs 강좌 11편. astrojs와 lucia를 이용해서 유저 인증 구현
January 16, 202412 minutes
안녕하세요?
오늘은 AstroJS 강좌 11편을 진행해 볼까 합니다.
지난 시간에 쿠키와 토큰을 이용한 유저 로그인을 구현했었는데요.
오늘은 똑같은 걸 Lucia를 이용해서 구현해 볼까 합니다.
전체 astrojs 강좌 목록입니다.
** 목 차 **
1. Lucia 소개
풀스택 개발에 있어 가장 중요한 게 Auth 부분인데요.
Next.js는 그 유명한 NextAuth가 있습니다.
Remix 진영에도 RemixAuth가 있는데요.
AstroJS를 지원하는 Auth 라이브러리가 별로 없는데요.
Lucia는 AstroJS, Next.js, Nuxtjs, SvelteKit 등 여러 가지의 프레임워크를 지원합니다.
기본적으로 유저네임 + 패스워드 방식뿐 아니라 OAuth도 지원합니다.
당연히 Typescript를 지원하고 있어 타입안정성을 쉽게 구현할 수 있습니다.
데이터베이스는 Adapter 방식을 이용하고 있어 여러 종류의 DB에 대한 코드는 공식 홈페이지에 있으니 참고 바랍니다.
Lucia는 세션 기반 라이브러리로 데이터베이스에는 세션정보를 저장하고, 해당 세션의 ID는 쿠키에 저장하여 관리합니다.
그래서 데이터베이스는 Prisma를 이용할 거고, 타입 정합성 검사는 Zod에 맡길 예정입니다.
2. Lucia 인증 방식
먼저, 사용자 가입을 완료했다고 전제했을 때, Lucia의 전체적인 흐름은 아래와 같습니다.
로그인 화면에서 유저네임과 패스워드로 로그인 Post 리퀘스트 전송.
Post 리퀘스트와 같이 넘어온 유저네임과 패스워드에 맞는 유저가 존재하는지 서버 측에서 확인
만약 유저가 존재한다면, 세션 데이터를 만들어서 데이터베이스에 저장하고, 만들어진 세션 데이터에 있는 세션 ID를 쿠키를 통해 클라이언트 사이드 쪽에서 저장합니다. (이게 로그인이 완료됐다는 뜻입니다.)
각 페이지에서 세션을 검증하는 미들웨어 함수를 구축하여 유저의 세션 정보에 따라 접근 가능한 페이지와 접근 불가능한 페이지를 구분하여 대응.
세션 검증 방식은 쿠키에 저장된 세션 ID를 꺼내 데이터베이스에 있는 세션을 획득하고,
이렇게 획득한 세션의 유효기간을 체크함. 유효기간에는 activePeriod와 idlePeriod 2개의 유효기간으로 관리되는데, activePeriod의 기한이 만료되어도 idlePeriod 기한내이면 세션의 유효기간을 리셋하는 방식으로 접근. 보통 activePeriod는 1일이고, idlePeriod는 2주간의 유효기간을 가집니다.
7.최종적으로 idlePeriod가 만료되면 해당 인증은 종료됩니다. 또한 쿠키가 만료되어도 인증이 종료되는데요. 쿠키 만료는 기본적으로 idlePeriod 유효기관과 동일합니다.
- 의도적으로 인증을 종료하고 싶은 경우 API 엔드포인트 같은 걸 만들어서 Post 리퀘스트로 세션을 무효화하거나 쿠키를 삭제하는 코드를 만들면 되는데, 그게 logout이 됩니다.
3. AstroJS 프로젝트 만들기
Astro는 ’npm create’를 지원하고 있어 아주 쉽게 프로젝트 템플릿을 구현할 수 있습니다.
npm create astro@latest astro-lucia
Need to install the following packages:
create-astro@4.7.1
Ok to proceed? (y)
astro Launch sequence initiated.
◼ dir Using astro-lucia as project directory
tmpl How would you like to start your new project?
Empty
deps Install dependencies?
Yes
ts Do you plan to write TypeScript?
Yes
use How strict should TypeScript be?
Strict
git Initialize a new git repository?
Yes
✔ Project initialized!
■ Template copied
■ Dependencies installed
■ TypeScript customized
■ Git initialized
next Liftoff confirmed. Explore your project!
Enter your project directory using cd ./astro-lucia
Run npm run dev to start the dev server. CTRL+C to stop.
Add frameworks like react or tailwind using astro add.
Stuck? Join us at https://astro.build/chat
╭─────╮ Houston:
│ ◠ ◡ ◠ Good luck out there, astronaut! 🚀
╰─────╯
➜ cd astro-lucia4. Prisma 설정
Prisma를 설치하고,
npm install prisma --save-devPrisma 초기화는 아래 명령어로 실행하면 됩니다.
npx prisma init --datasource-provider sqlite
✔ Your Prisma schema was created at prisma/schema.prisma
You can now open it in your favorite editor.
warn You already have a .gitignore file. Don't forget to add `.env` in it to not commit any private information.
Next steps:
1. Set the DATABASE_URL in the .env file to point to your existing database. If your database has no tables yet, read https://pris.ly/d/getting-started
2. Run prisma db pull to turn your database schema into a Prisma schema.
3. Run prisma generate to generate the Prisma Client. You can then start querying your database.
More information in our documentation:
https://pris.ly/d/getting-started위와 같이 초기화하면 prisma 디렉토리와 ‘.env’ 파일이 생성됩니다.
prisma 디렉토리에는 schema.prisma 파일이 자동적으로 생길 겁니다.
테스트를 위한 개발 서버를 꾸릴 예정이라 Sqlite3를 이용했습니다.
5. Model 설정
Lucia를 이용한 세션 관리를 위해 아래와 같이 최소한의 모델로 설정하겠습니다.
// This is your Prisma schema file,
// learn more about it in the docs: https://pris.ly/d/prisma-schema
generator client {
provider = "prisma-client-js"
}
datasource db {
provider = "sqlite"
url = env("DATABASE_URL")
}
model User {
id String @id @unique
auth_session Session[]
key Key[]
}
model Session {
id String @id @unique
user_id String
active_expires BigInt
idle_expires BigInt
user User @relation(references: [id], fields: [user_id], onDelete: Cascade)
@@index([user_id])
}
model Key {
id String @id @unique
hashed_password String?
user_id String
user User @relation(references: [id], fields: [user_id], onDelete: Cascade)
@@index([user_id])
}Lucia에서 사용할 모델은 User, Session, Key로 되어 있고, 최신 트렌드에 따라 User와 Key 부분을 따로 분리했습니다.
이제 스키마를 push 해서 Sqlite 테이블을 만들도록 하겠습니다.
npx prisma db push
Environment variables loaded from .env
Prisma schema loaded from prisma/schema.prisma
Datasource "db": SQLite database "dev.db" at "file:./dev.db"
SQLite database dev.db created at file:./dev.db
🚀 Your database is now in sync with your Prisma schema. Done in 15ms
Running generate... (Use --skip-generate to skip the generators)
added 1 package, and audited 503 packages in 5s
183 packages are looking for funding
run `npm fund` for details
found 0 vulnerabilities
✔ Generated Prisma Client (v5.8.0) to ./node_modules/@prisma/client in 47msPrisma Client까지 만들어졌네요.
Prisma는 Studio라는 아주 편한 UI를 제공해 주고 있어, Prisma DB의 작성에 아주 큰 도움이 되는데요.
npx prisma studio6. Lucia 설치 및 코드 작성
Lucia와 Prisma 어댑터를 같이 설치하겠습니다.
npm i lucia @lucia-auth/adapter-prisma당연히 세션 관련이니까 Astro를 서버사이드 렌더링으로 바꿔야 합니다.
// astro.config.mjs
import { defineConfig } from 'astro/config';
// https://astro.build/config
export default defineConfig({
output: 'server',
});만약 다음과 같은 에러나 경고가 나온다면 그건 바로 SSR 모드로 설정하지 않아서 일겁니다.
11:30:34 [WARN] `Astro.request.headers` is not available in "static" output mode. To enable header access: set `output: "server"` or `output: "hybrid"` in your config file.6.1. lucia.ts 파일 만들기
이제 Asto 코드에서 Lucia에 접근할 수 있는 lucia.ts 파일을 만들 건데요.
src 폴더 밑에 lib 폴더를 만들고 그 밑에 만들겠습니다.
// src/lib/lucia.ts
import { lucia } from 'lucia';
import { astro } from 'lucia/middleware';
import { prisma } from '@lucia-auth/adapter-prisma';
import { PrismaClient } from '@prisma/client';
const client = new PrismaClient();
export const auth = lucia({
adapter: prisma(client),
env: import.meta.env.DEV ? 'DEV' : 'PROD',
middleware: astro(),
});
export type Auth = typeof auth;타입정보까지 export하는 거는 Drizzle ORM과 많이 비슷합니다.
이제 lucia를 이용해서 auth 객체를 만들었으니까 앞으로 이 auth 객체를 이용해서 세션 관련 작업을 진행하면 됩니다.
6.2. lucia 관련 타입 env.d.ts 설정
우리가 schema.prisma 파일에서 정의한 User, Session 모델의 타입을 정확하게 검색할 수 있도록 env.d.ts 파일에 lucia 관련 정보를 정의해야 합니다.
// src/env.d.ts
/// <reference types="astro/client" />
/// <reference types="lucia" />
declare namespace Lucia {
type Auth = import('./lib/lucia').Auth;
type DatabaseUserAttributes = {};
type DatabaseSessionAttributes = {};
}6.3. middleware를 이용해서 auth 객체 전역화 시키기
Astro에서 객체를 전역화 시키는 건 context.locals를 이용하면 아주 쉬운데요.
그래서 매 번 Request가 발생할 때마다 변경된 auth 객체를 context.locals에 저장해야 하는데요.
이때 필요한 게 미들웨어입니다.
Astro에서는 미들웨어는 src 폴더 밑에 middleware.ts 파일을 만들어 구성할 수 있습니다.
import { auth } from "./lib/lucia";
import { defineMiddleware } from "astro:middleware";
export const onRequest = defineMiddleware((context, next) => {
context.locals.auth = auth.handleRequest(context);
return next();
});이렇게 하면 context.locals.auth의 타입이 부정확하다고 나오는데요.
다시 ’env.d.ts’ 파일에 아래 부분을 추가해야 합니다.
// src/env.d.ts
/// <reference types="astro/client" />
/// <reference types="lucia" />
declare namespace Lucia {
type Auth = import("./lib/lucia").Auth;
type DatabaseUserAttributes = {};
type DatabaseSessionAttributes = {};
}
///
declare namespace App {
interface Locals {
auth: import("lucia").AuthRequest;
}
}이제 middleware.ts에서 auth 부분의 타입 에러가 없어질 겁니다.
7. AstroJS의 Layout 페이지 만들기
본격적인 웹페이지 구성에 들어가 보겠습니다.
AstroJS에서는 무조건 Layout 페이지를 만드는 게 아주 편한데요.
그리고, 우리가 만들 페이지의 링크 부분을 넣도록 하겠습니다.
---
import { ViewTransitions } from "astro:transitions";
---
<html lang="ko">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1" />
<title>Astro</title>
<ViewTransitions />
</head>
<body>
<nav>
<ul>
<li><a href="/">Home</a></li>
<li><a href="/login">Login</a></li>
<li><a href="/signup">Signup</a></li>
<li><a href="/dashboard">Dashboard</a></li>
</ul>
</nav>
<slot />
</body>
</html>이제 src/pages 폴더의 index.astro 파일을 손봐야 하는데요.
// // src/pages/index.astro
---
import Layout from "../layouts/Layout.astro";
---
<Layout>
<h1>Home</h1>
</Layout>이왕 만드는 거 src/pages/dashboard 폴더를 만들고 그리고 index.astro 파일을 아래와 같이 똑같이 만들어 줍시다.
// src/pages/dashboard/index.astro
---
import Layout from "../../layouts/Layout.astro";
---
<Layout>
<h1>Dashboard</h1>
</Layout>이제 개발 서버를 돌려 전체적인 틀이 작동하는지 보면 됩니다.
위와 같이 home, dashboard 링크는 정상작동합니다.
그러나 아직 login과 signup 링크는 작동하지 않는데요.
이제 만들어 보겠습니다.
8. Signup 페이지 만들기
먼저, Signup 페이지를 만들기 위해 ‘src/pages’ 폴더 밑에 ‘signup.astro’ 파일을 만들겠습니다.
먼저, 타입 정합성 검사를 위해 ‘zod’ 라이브러리를 설치하겠습니다.
npm i zod본격적인 signup.astro 파일의 코드입니다.
---
import { LuciaError } from "lucia";
import Layout from "../layouts/Layout.astro";
import { auth } from "../lib/lucia";
import z from "zod";
let usernameInput = "";
let errorMessages: z.ZodIssue[] = [];
let errorMessage: string | null = null;
if (Astro.request.method === "POST") {
const formData = await Astro.request.formData();
const username = formData.get("username");
const password = formData.get("password");
if (typeof username === "string") usernameInput = username;
const result = z
.object({
username: z.string().min(4).max(31),
password: z.string().min(8),
})
.safeParse({ username, password });
if (!result.success) {
errorMessages = result.error.errors;
Astro.response.status = 400;
} else {
try {
const user = await auth.createUser({
key: {
providerId: "username",
providerUserId: result.data.username.toLowerCase(),
password: result.data.password,
},
attributes: {},
});
const session = await auth.createSession({
userId: user.userId,
attributes: {},
});
Astro.locals.auth.setSession(session);
return Astro.redirect("/dashboard", 302);
} catch (e) {
if (e instanceof LuciaError && e.message === "AUTH_DUPLICATE_KEY_ID") {
errorMessage = "Username already taken";
Astro.response.status = 400;
} else {
errorMessage = "Internal Server Error";
Astro.response.status = 500;
}
}
}
}
---
<Layout>
<h1>Sign up</h1>
<form method="post">
<label for="username">Username</label>
<input name="username" id="username" value={usernameInput} />
<br />
<label for="password">Password</label>
<input type="password" name="password" id="password" />
<br />
{
errorMessages.length > 0 &&
errorMessages.map((error) => (
<p>
{error.path[0]}: {error.message}
</p>
))
}
<p>{errorMessage}</p>
<button type="submit">가입하기</button>
</form>
<br />
<a href="/login">Sign in</a>
</Layout>이제 테스트를 위해 username과 password에 넣고 테스트해 봅시다.
위 그림과 같이 zod 부분이 정확하게 작동하고 있네요.
Lucia가 createUser하는 방식은 key를 이용한 방식인데요.
Lucia가 말하는 key는 유저와 유저를 가리키는 레퍼런스 사이의 관계를 얘기합니다.
조금은 어려울 수 있는데요.
우리가 사용한 Key 방식은 전통적인 유저네임과 패스워드 방식입니다.
그래서 아래와 같이 작성한 거죠.
const user = await auth.createUser({
key: {
providerId: "username",
providerUserId: result.data.username.toLowerCase(),
password: result.data.password,
},
attributes: {},
});전통적인 username/password 방식을 Lucia에서는 Key의 ‘providerId’라고 합니다.
만약 email/password 방식이라면 Key의 ‘providerId’는 ’email’이 되는 거죠.
OAuth의 경우 만약 Github을 이용한다면 Github user id가 해당되는 거죠.
NextAuth와는 조금 다른 개념이라 처음에는 어렵지만 공식 문서를 자세히 살펴보면 많은 예가 있으니까 참고 바랍니다.
key 부분의 providerUserId와 password 부분은 실제 유저가 입력한 username과 password를 입력하면 됩니다.
zod의 safeParse 함수를 이용했기 때문에 관련 값은 result 객체에 모두 다 있으니까 거기서 username과 password를 가져오면 됩니다.
지금하고 있는 게 ‘signup’ 가입하기입니다.
그래서 createUser 함수를 사용했고, 그다음 가입한 유저정보로 세션을 만들어 로그인한 상태로 바꿔야 하는데요.
그래서 사용한 함수가 auth.createSession 함수입니다.
const session = await auth.createSession({
userId: user.userId,
attributes: {},
});세션 정보에는 당연히 userId만 들어가면 됩니다.
Session을 작성한 후, middleware로부터 받은 Astro.locals.auth.setSession(AuthRequest.setSession)을 이용하여 쿠키를 작성합니다.
쿠키에는 Session에서 만든 SessionId가 포함됩니다.
쿠키를 만든 후 /dashboard로 리디렉션 합니다.
그 외 에러핸들링은 쉽게 이해할 수 있을 거라 판단되어 넘어가도록 하겠습니다.
테스트해 볼까요?
터미널을 하나 더 열고 ’npx prisma studio’를 실행해서 prisma db 내용을 점검하도록 하겠습니다.
위 두 그림처럼 Key와 User 부분이 제대로 작동하네요.
Session 부분을 볼까요?
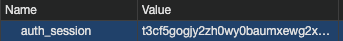
위에서 보시면 Session의 id가 ’t3cf5….‘로 시작하는 문자열인데요.
크롬 개발 창의 Application에 들어가서 쿠키를 검색해 볼까요?
개발 서버니까 ‘http://localhost:4321’ 쪽에 아래와 같이 ‘auth_session’ 이름으로 쿠키가 저장되어 있습니다.
쿠키의 Value를 보시면 Prisma Studio에서 본 Session Id 값이 그대로 들어가 있네요.
지금까지 설명했던 Lucia의 세션 관리 방식이 제대로 들어맞고 있습니다.
가입하기는 성공적으로 작성했네요.
단, 여기서 추가할 게 있다면 그건 현재 로그인 상태를 체크해서 로그인되어 있다면 dashboard로 이동하는 겁니다.
로그인된 사람이 다시 가입할 리가 없기 때문이죠.
로그인 상태 검사는 아래와 같이 하면 됩니다.
// 코드의 마지막에
const session = await Astro.locals.auth.validate();
if (session) return Astro.redirect("/dashboard", 302);위와 같이 하면 이제 로그인한 상태에서 ‘/signup’ 페이지로 가면 자동으로 ‘/dashboard’ 페이지로 이동하게 됩니다.
9. login 페이지 만들기
로그인은 signup과 거의 똑같은데요.
---
import { LuciaError } from 'lucia';
import Layout from '../layouts/Layout.astro';
import { auth } from '../lib/lucia';
import z from 'zod';
let usernameInput = '';
let errorMessages: z.ZodIssue[] = [];
let errorMessage: string | null = null;
if (Astro.request.method === 'POST') {
const formData = await Astro.request.formData();
const username = formData.get('username');
const password = formData.get('password');
if (typeof username === 'string') usernameInput = username;
const result = z
.object({
username: z.string().min(4).max(31),
password: z.string().min(8),
})
.safeParse({ username, password });
if (!result.success) {
errorMessages = result.error.errors;
Astro.response.status = 400;
} else {
try {
const key = await auth.useKey(
'username',
result.data.username.toLowerCase(),
result.data.password
);
const session = await auth.createSession({
userId: key.userId,
attributes: {},
});
Astro.locals.auth.setSession(session);
return Astro.redirect('/dashboard', 302);
} catch (e) {
if (
e instanceof LuciaError &&
(e.message === 'AUTH_INVALID_KEY_ID' ||
e.message === 'AUTH_INVALID_PASSWORD')
) {
errorMessage = 'Incorrect username or password';
Astro.response.status = 400;
} else {
errorMessage = 'Internal Server Error';
Astro.response.status = 500;
}
}
}
}
const session = await Astro.locals.auth.validate();
if (session) return Astro.redirect('/dashboard', 302);
---
<Layout>
<h1>Login</h1>
<form method="post">
<label for="username">Username</label>
<input name="username" id="username" value={usernameInput} />
<br />
<label for="password">Password</label>
<input type="password" name="password" id="password" />
<br />
{errorMessages.length > 0 &&
errorMessages.map((error) => (
<p>
{error.path[0]}:{error.message}
</p>
))}
<p>{errorMessage}</p>
<button type="submit">로그인하기</button>
</form>
<br />
<a href="/signup">Sign UP</a>
</Layout>위 코드에서 눈 여겨봐야할 부분은 useKey 부분입니다.
const key = await auth.useKey(
'username',
result.data.username.toLowerCase(),
result.data.password
);login 방식은 먼저, auth.useKey 함수를 이용해서 유저가 form에서 입력한 username과 password을 ‘providerId’를 ‘username’ 방식으로 검증하게 됩니다.
데이터베이스내의 정보와 일치하면 일치하는 key 정보를 리턴하게 됩니다.
key 데이터는 userId가 포함되어 있어 createSession 함수에 사용할 수 있습니다.
그리고 마찬가지로 Astro.locals.auth.setSession() 함수를 이용해서 쿠키를 작성하게 되는겁니다.
10. Dashboard 페이지 설정
로그인한 상태를 Dashboard에 반영해 볼까요?
session이 없으면 login 페이지로 이동하고 session이 있다면 session에서 user와 userId를 가져와서 화면에 출력하는 겁니다.
---
import Layout from "../../layouts/Layout.astro";
const session = await Astro.locals.auth.validate();
if (!session) return Astro.redirect("/login", 302);
---
<Layout>
<h1>Dashboard</h1>
<div>{session.user.userId}</div>
</Layout>아래 그림처럼 userId가 제대로 나타나고 있네요.
11. logout 구현
로그인하면 대시보드 페이지로 이동한다고 했으니까, 대시보드 페이지 안에 로그아웃 기능을 추가하겠습니다.
기타 서버사이드 렌더링에서 그렇듯 로그아웃은 HTTP POST 리퀘스트를 보내는 겁니다.
대시보드 폴더의 index.astro 파일을 아래와 같이 바꿔줍니다.
---
import Layout from "../../layouts/Layout.astro";
const session = await Astro.locals.auth.validate();
if (!session) return Astro.redirect("/login", 302);
---
<Layout>
<h1>Dashboard</h1>
<div>{session.user.userId}</div>
<form method="post" action="/logout">
<button type="submit">로그아웃</button>
</form>
</Layout>HTTP POST 리퀘스트의 목적지가 바로 “/logout” 경로인데요.
pages 폴더 밑에 logout.ts 파일을 만들고 POST 리퀘스트를 처리하는 로직을 만들면 됩니다.
이 파일의 확장자가 왜 ‘.ts’일까요?
바로 UI 부분이 없고 로직만 있기 때문입니다.
// src/pages/logout.ts
import { auth } from "../lib/lucia";
import type { APIRoute } from "astro";
export const POST: APIRoute = async (context) => {
const session = await context.locals.auth.validate();
if (!session) {
return new Response("Unauthorized", {
status: 401,
});
}
await auth.invalidateSession(session.sessionId);
context.locals.auth.setSession(null);
return context.redirect("/login", 302);
};로그아웃의 로직은 먼저, Astro의 POST API 엔도포인트로의 작성인데요.
POST 리퀘스트를 처리하기 때문에 이름이 POST입니다.
먼저, session 정보를 얻고 나서 만약 session이 없다면 ‘Unauthorized’ 메시지와 함께 401 Response를 보내면 됩니다.
session이 있다면 invalidateSesion 함수로 세션을 무력화하고, 그다음 context.locals.auth.setSession(null) 명령어로 클라이언트의 쿠키를 무력화시킵니다.
마지막으로 ‘/login’ 페이지로 이동하면 끝인 거죠.
테스트해보십시오.
잘 될 겁니다.
지금까지 AstroJS와 Lucia를 이용한 유저 가입, 로그인을 구현해 봤습니다.
Lucia가 조금은 생소할지 모르지만 Astro를 사용한다면 꼭 배워야 할 인증 라이브러리임에는 틀림없네요.
그럼.